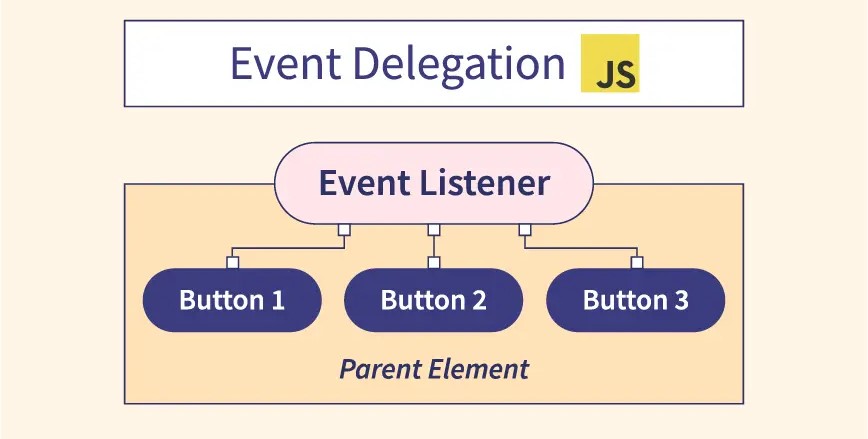
Event delegation is a programming pattern in JavaScript where a single event listener is attached to a parent element instead of multiple event listeners on individual child elements. This works because of event bubbling, where events triggered on child elements propagate (or "bubble up") to their ancestors.
Why use event delegation?
- Performance: Fewer event listeners mean less memory usage and better performance.
- Dynamic content: It handles events on elements that are added to the DOM after the event listener is attached.
Example
Suppose you have a list of items and want to respond to clicks on any item:
HTML:
<ul id="myList">
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ul>
Without delegation (inefficient for large/dynamic lists):
document.querySelectorAll('#myList li').forEach(item => {
item.addEventListener('click', () => {
console.log('Item clicked');
});
});
With event delegation (better):
document.getElementById('myList').addEventListener('click', function(event) {
if (event.target.tagName === 'LI') {
console.log('Item clicked:', event.target.textContent);
}
});
In this delegated version, a single listener on the <ul> handles clicks for all <li> elements—even ones added later.
Key Points:
- Relies on event bubbling.
- Use event.target to find which child was actually clicked.
- Often used for lists, tables, or any UI elements where children are dynamic.
See More Related Blog
What is the difference between event.preventDefault() and event.stopPropagation()?
-

- by Mcs
event.preventDefault() is used to prevent the browser from executing the default action associated with the event. It tells the browser not to perform its default…
Event Bubbling in JavaScript – How Event Propagation Works with Examples
-

- by Mcs
Event Bubbling in JavaScript is the process where an event starts at the target element and then bubbles up to its parent elements. This blog explains how event…
How to Store, Read, Update & Delete Cookies in JavaScript
-

- by Mcs
JavaScript cookies are small data stored on a user's device by a web browser. These cookies play a crucial role in web development, enabling websites to store and…
What is sessionStorage?
-

- by Mcs
JavaScript sessionStorage is a web storage technique that stores data for the duration of a page session. The sessionStorage object lets you store key/value pairs in the…
What is localStorage?
-

- by Mcs
JavaScript localStorage is a feature that lets you store data in your browser using key-value pairs. The data stays saved even after you close the browser, so it can be…
Local Storage vs Session Storage vs Cookies: Complete Comparison (2025)
-

- by Mcs
The HTTP protocol is one of the most important protocols for smooth communication between the server and the client. The main disadvantage of the HTTP protocol is that…
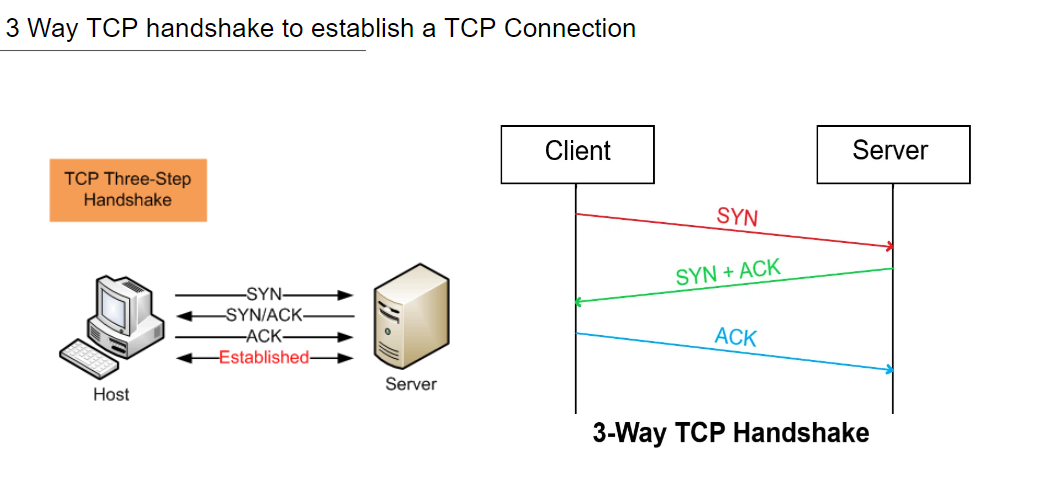
What is the TCP 3-Way Handshake
-

- by Mcs
The TCP 3-Way Handshake is a fundamental process that establishes a reliable connection between two devices over a TCP/IP network. It involves three steps: SYN (…
What is Fabric.js ?
-

- by Mcs
Fabric.js is a powerful JavaScript library used to work with HTML5 <canvas>. It makes it easy to draw, move, scale, rotate, and interact with shapes, images, and…
What is Three.js ?
-

- by Mcs
Three.js is a JavaScript 3D graphics library that makes it easy to create and display 3D graphics in the browser using WebGL.
What is p5.js ?
-

- by Mcs
p5.js is a JavaScript library that makes it easy to create graphics, animations, and interactive experiences in the browser using simple code.
what is JavaScript Graphics ?
-

- by Mcs
JavaScript Graphics refers to the ability to create and manipulate visual content (like shapes, images, animations, and interactive visual effects) on a webpage using…
JS vs jQuery
-

- by Mcs
JavaScript is a full-fledged, independent programming language, while jQuery is a JavaScript library. This means jQuery is built on top of JavaScript, designed to…
What is JSON ?
-

- by Mcs
JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation.It is a lightweight format for storing and exchanging data, and it’s easy for both humans and machines to read.
What is Web API ?
-

- by Mcs
A Web API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of tools and rules that allows different software (like your JavaScript code) to communicate with web servers or…
What is Browser Object Model (BOM) ?
-

- by Mcs
The Browser Object Model (BOM) in JavaScript is a collection of objects that allow JavaScript to interact with the web browser itself, beyond just the content of the web…
What is DOM ?
-

- by Mcs
The Document Object Model (DOM) in JavaScript is a programming interface for web documents (HTML or XML).
What is object ?
-

- by Mcs
An object in JavaScript is a special data type that allows you to store data in key-value pairs.
Set Date Methods in js
-

- by Mcs
In JavaScript, "Set Date Methods" refer to a collection of methods available on the Date object that allow for the modification of specific components of a…
Get Date Methods in js
-

- by Mcs
Date Get Methods refer to the functions available in programming languages, particularly in JavaScript, that allow you to extract specific components of a date and time…
What is array ?
-

- by Mcs
An array is a special type of variable that can store multiple values in a single variable.
Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS
-

- by Mcs
HTTPS is just HTTP with encryption. The primary distinction between these two names is that HTTPS is more secure than HTTP since it uses TLS (SSL) encryption for all…
What is function ?
-

- by Mcs
A function in JavaScript is a block of code designed to perform a specific task. You can reuse a function wherever you need it, which helps keep your code clean and…
Types of Loops in JavaScript
-

- by Mcs
In JavaScript, a loop is a control structure that allows for the repeated execution of a block of code until a specified condition is met. Loops are fundamental for…
conditional statements in javascript
-

- by Mcs
Conditional statements in JavaScript allow for the execution of different blocks of code based on whether a specified condition evaluates to true or false. These…
What is operator in js ?
-

- by Mcs
In JavaScript, an operator is a special symbol or keyword that performs an operation on one or more values, called operands. Operators are fundamental to building…
data types in javascript
-

- by Mcs
JavaScript data types categorize the different kinds of values that can be stored and manipulated within the language. These are broadly divided into two categories:…
What is variables ?
-

- by Mcs
In JavaScript, variables are named containers used to store data values. They act as placeholders for information that can be accessed and manipulated throughout a…
Output Show Method in javascript
-

- by Mcs
JavaScript offers several methods to display output, each suited for different purposes:
difference between es5 and es6 in javascript
-

- by Mcs
ES5 (ECMAScript 5) and ES6 (ECMAScript 2015) represent significant milestones in the evolution of JavaScript, introducing distinct features and paradigms for writing…
what is Javascript ?
-

- by Mcs
JavaScript is the world's most popular programming language. JavaScript is the Programming Language for the Web. JavaScript can update and change both HTML and CSS…
@ Mcs. All rights reserved



































Comments
Add new comment