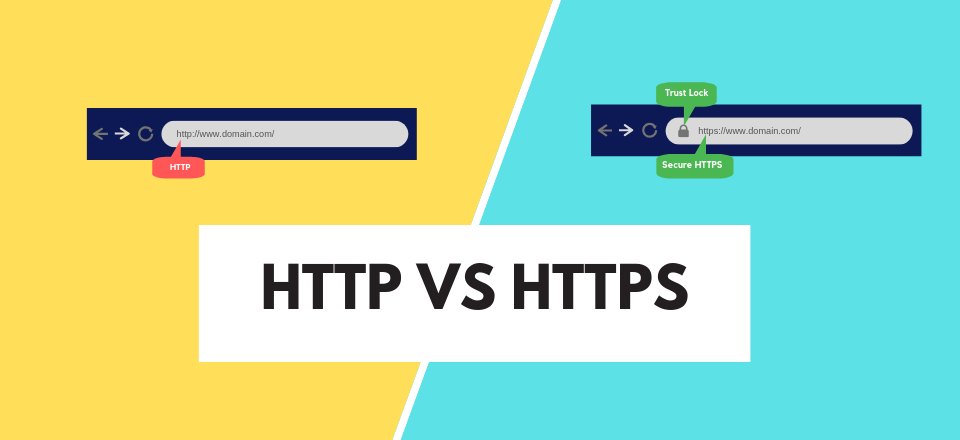
Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a protocol used which transfer hypertext over the Web.
- Due to its simplicity, HTTP has been the most widely used protocol for data transfer over the Web, but the data (i.e,. hypertext) exchanged using HTTP isn’t as secure as we would like it to be.
- In fact, hyper-text exchanged using HTTP goes as plain text i.e., anyone between the browser and server can read it relatively easily if one intercepts this exchange of data.
- The acronym for Hypertext Transfer Protocol is HTTP.
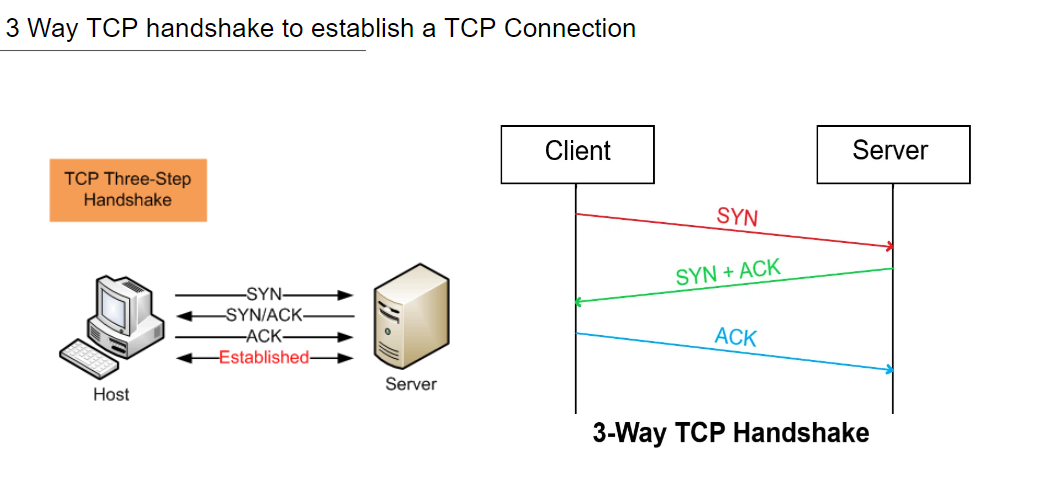
- The web server delivers the desired data to the user in the form of web pages when the user initiates an HTTP request through their browser. Above the TCP layer lies an application layer protocol called HTTP. It has given web browsers and servers certain standard principles that they can use to talk to one another.
- Because each transaction on the HTTP protocol is carried out independently of the others and without reference to the history, the connection between the web browser and the server ends after the transaction is finished. This makes HTTP a stateless protocol.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
- Because fewer connections are running at once, it delivers reduced CPU and memory utilization.
- It allows requests and answers to be pipelined via HTTP.
- Because there are fewer TCP connections, it provides less network congestion.
- During the first stage of connection establishment, handshakes are exchanged. Because there is no handshaking, it provides lower latency for subsequent requests.
- Without terminating the TCP connection, it reports problems.
Disadvantages of HTTP
- It is applicable to point-to-point connections.
- It isn't mobile-friendly.
- It sends more data than needed.
- It doesn't provide trustworthy exchange (in the absence of retry mechanism).
- When the client receives all the data it requires, the connection is not terminated. Therefore, the server won't be accessible during this time.
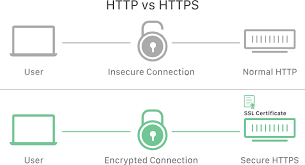
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS)
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extended version of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It is used for secure communication.
- In HTTPS, the communication protocol is encrypted using Transport Layer Security.
- HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure.
- While HTTPS guarantees data security, the HTTP protocol does not provide data security.
- As a result, HTTPS can be defined as a secure variant of the HTTP protocol. Data can be transferred using this protocol in an encrypted format.
- In most cases, the HTTPS protocol must be used while entering bank account information.
- The HTTPS protocol is mostly utilised in situations when entering login credentials is necessary. Modern browsers like Chrome distinguish between the HTTP and HTTPS protocols based on distinct markings.
- HTTPS employs an encryption mechanism called Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), also known as Transport Layer Security, to enable encryption.
Advantages of HTTPS
- Provides in-transit data security.
- Shields your website from data breaches, phishing, and MITM attacks.
- Increases the visitors' trust to your website.
- Eliminates the "NOT Secure" alerts.
- Assist you in raising your website's ranking.
Disadvantages of HTTPS
- When switching to HTTPS, an SSL certificate needs to be bought. Even though website hosts often give SSL certificates, these should be renewed annually by paying a charge.
- Encrypting and decrypting data across HTTPS connections requires a lot of computation.
- There will be issues with caching some information over HTTPS. Public caching of those that previously took place won't happen again.
- Certain proxy servers and firewalls prevent users from accessing HTTPS websites. Both deliberate and inadvertent actions might result from this.
- If there are configuration issues, HTTP will be used by your website to obtain files rather than HTTPS.
| HTTP | HTTPS | |
| Stands for | Hypertext Transfer Protocol | Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure |
| Underlying Protocols | HTTP/1 and HTTP/2 use TCP/IP. HTTP/3 uses QUIC protocol. | Uses HTTP/2 with SSL/TLS to further encrypt the HTTP requests and responses |
| Port | Default Port 80 | Default Port 443 |
| Used for | Older text-based websites | All modern websites |
| Security | No additional security features | Uses SSL certificates for public-key encryption |
| Benefits | Made communication over the internet possible | Improves website authority, trust, and search engine rankings |




































Comments
Add new comment