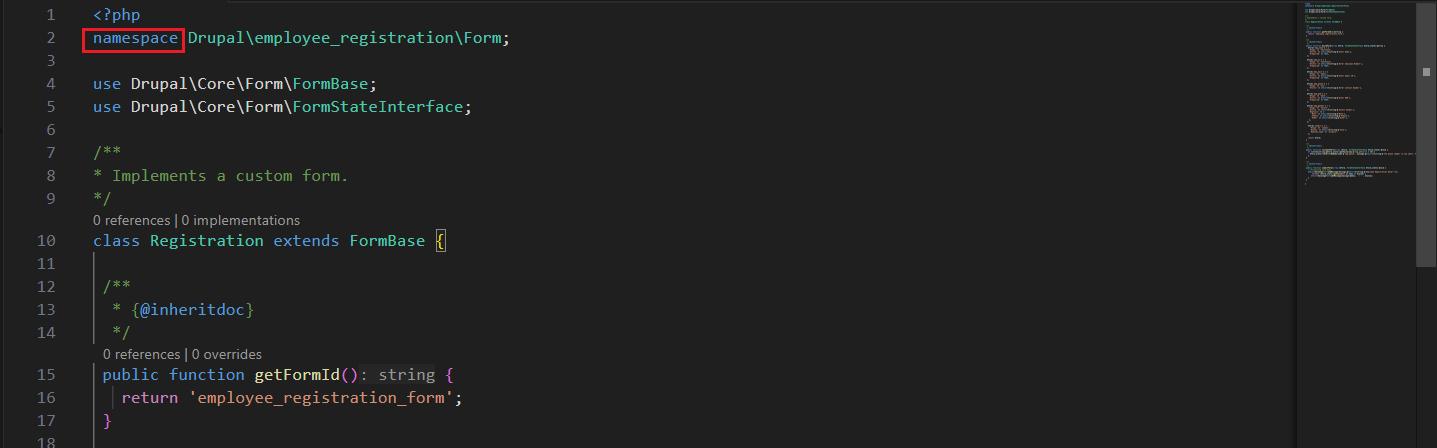
What is a Namespace in PHP?
A namespace in PHP is a way to group related code and avoid name conflicts between classes, functions, or constants.
Why Do We Need Namespaces?
magine you're working on a large project (like Drupal) with hundreds of modules. What happens if two modules define a class called UserController?
Without namespaces, PHP wouldn't know which one you're referring to—leading to fatal errors.
Namespaces Solve This Problem
Namespaces work like folders in your file system:
// File: modules/custom/my_module/src/Controller/MyController.php
namespace Drupal\my_module\Controller;
class MyController {
// Your controller code here
}
In this case, even if another module has a class called MyController, it won't clash because it's in a different namespace.
Analogy
Think of namespaces like:
- Email addresses: You can have john@gmail.com and john@yahoo.com — the usernames are the same, but the domain keeps them separate.
- Folders: You can have a file named invoice.pdf in multiple folders. As long as they’re in different folders, they don’t conflict.
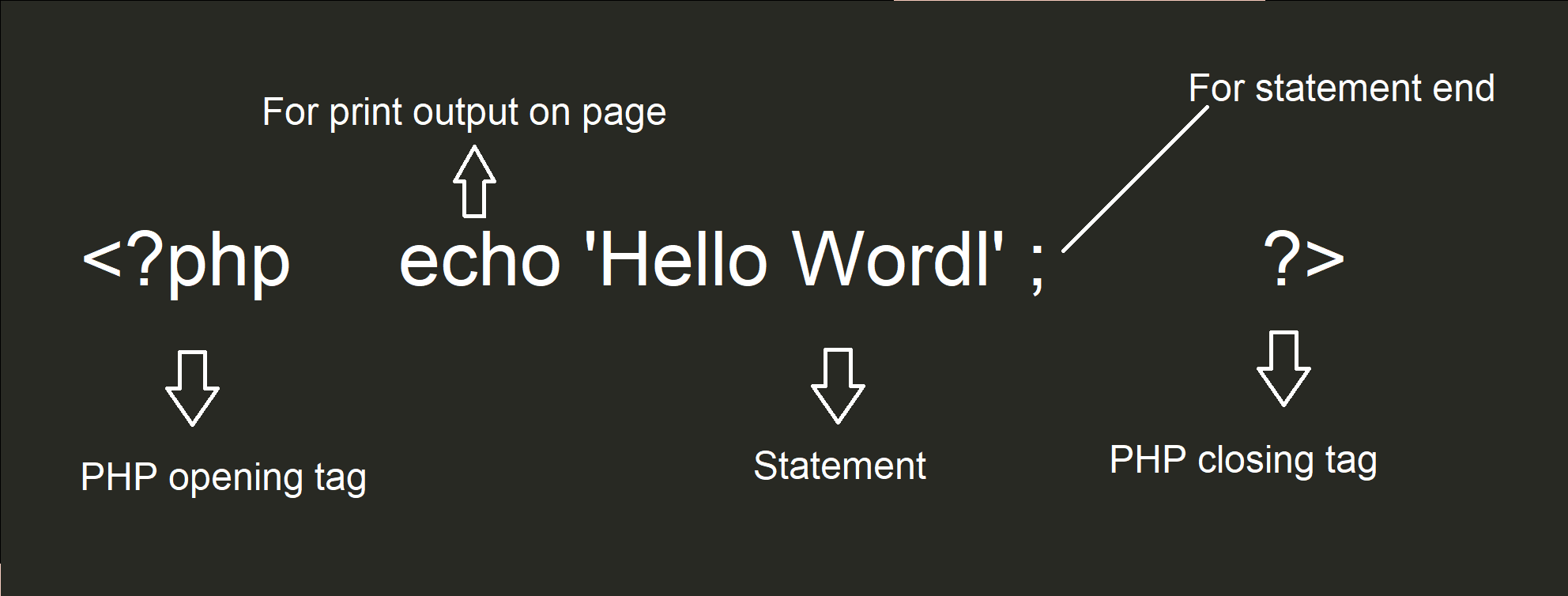
PHP Namespace Syntax
Here's a basic syntax:
<?php
namespace MyProject\SubNamespace;
class MyClass {
public function sayHello() {
return "Hello from MyClass!";
}
}
To use this class somewhere else:
use MyProject\SubNamespace\MyClass;
$obj = new MyClass();
echo $obj->sayHello();
Namespaces in Drupal
Drupal follows the PSR-4 autoloading standard, which means:
- The namespace matches the folder structure.
- Drupal automatically loads classes based on their namespace.
Example:
namespace Drupal\my_module\Controller;
use Drupal\Core\Controller\ControllerBase;
class MyController extends ControllerBase {
public function content() {
return ['#markup' => 'Hello Drupal with namespaces!'];
}
}
Key Takeaways
- Namespaces prevent naming conflicts.
- They group related code logically.
- In Drupal, they follow the Drupal\module_name\SubFolder structure.
- Understanding them is essential for writing modern Drupal code.














Comments
Add new comment